The Starship Startups - H+ Weekly - Issue #408
This week - GPT-4 and sparks of AGI; the age of AI has begun; mammoth meatballs; Levi hires digital models; new AI products and services from Nvidia; and more!
Although space exploration is not the main subject of H+ Weekly, it is a vital area that, if done correctly, will allow humanity to flourish.
In this guest post, Ben Lachman and Andrew Cantino from The Orbital Index shine a light on an interesting development in the space industry - the rise of startups betting hard on SpaceX’s Starship to succeed.
If you want to stay up-to-date on what is going on in the space industry and space exploration, check out The Orbital Index newsletter. Thank you Ben and Andrew for sharing your experience and insights.
Guest posts represent the opinions of the author and not necessarily mine.
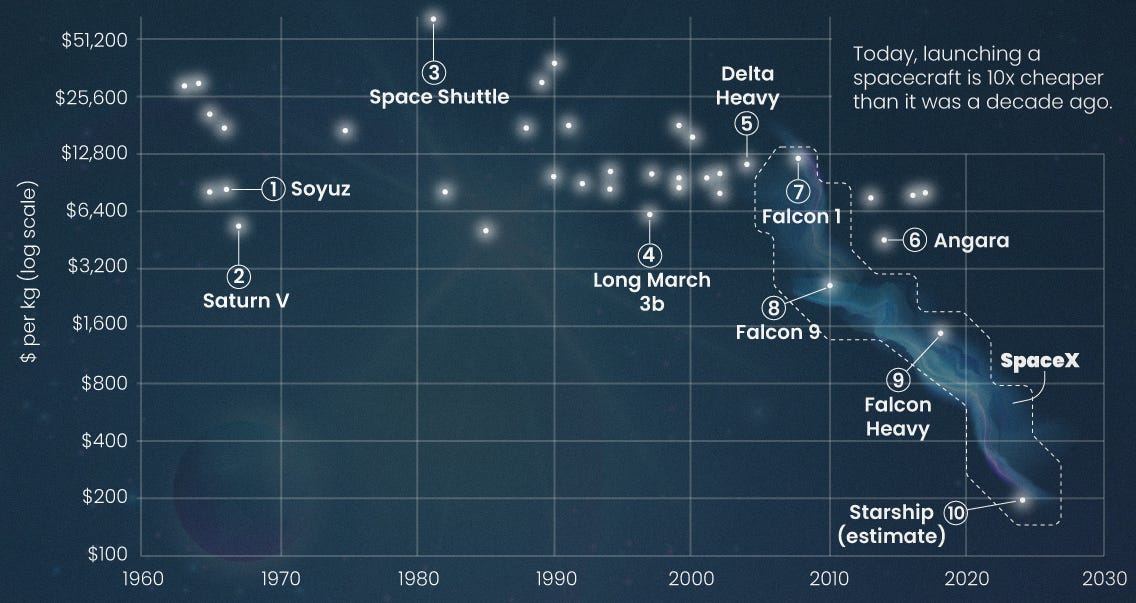
A macro-trend gaining traction is newspace startups formed on the assumption of Starship’s success, a world in which a whole new scale of in-space systems will be possible and cost-effective (cf. Casey Handmer’s 2021 admonishment of NASA for not planning for this future). SpaceX is targeting a cost per kilogram of $50-$500 for Starship, representing a one- or two-order-of-magnitude reduction from Falcon’s current industry-leading $2,300/kg (for expendable launches on Falcon Heavy) to $5,500/kg (for Falcon 9 rideshare payloads).
Other in-development reusable launch systems are targeting low costs as well (Terran-R, Neutron, and others), which only makes this low-launch cost future more likely, although not everyone sees it panning out.
To take full advantage of this potential industry sea-change and leverage first mover advantage, startups must start development today to be ready when Starship becomes commercially operational. (No prediction from us on when that will be, but the program now feels unlikely to fail completely… as some suggested when it was first announced.)
The most recent of this new breed of startups to emerge from stealth mode is K2 Space, building large-scale satellite busses that are specifically designed for a “post-Starship future”—they’re developing large busses in the style of development popularized by cubesats (commercial off-the-shelf components, standardized sizes, etc.) but optimizing for low cost to orbit and economies of scale. As part of their reveal, K2 announced Mega-class (1 ton of customer payload at ~$15M) and (future) Giga-class (15 tons at ~$30M) busses which they believe will support large power budgets (20kW+) and markedly lower development costs compared to traditional bespoke GEO sats or high-budget/complexity deep space missions. K2 has raised an $8.5M seed round led by First Round Capital and Republic Capital.
Other startups that are betting on this Starship-enabled future are likely K2 competitor Apex Space, Impulse Space (vacuum-optimized propulsion and cislunar fuel service), Varda (high-value in-space manufacturing and re-entry), Vast (artificial-gravity commercial space stations), perhaps Solestial (thin, flexible nextgen in-space solar panels), Ethos (lunar water mining for propellant), AstroForge (betting that water will decrease in value while space-sourced metal values will stay high, due to Starship’s payload capabilities), and other still-stealth startups we know and love.
(Related: Some satellite parts suppliers are also betting on this future—where economies of scale will mean many thousands of a part are produced instead of the mostly hand-made tens to hundreds of similar parts produced today.)
This article was originally published on The Orbital Index.
🦾 More than a human
Have scientists found a “brake pedal” for aging?
One promising technique to combat ageing is reducing inflammation. Many diseases of old age are associated with chronic, low-level inflammation in the brain, organs, joints, and circulatory system — sometimes called “inflammageing.” A new discovery suggests that a protein in the brain may be a switch for controlling inflammation and, with it, a host of symptoms of ageing.
🧠 Artificial Intelligence
Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4
In this paper, researchers from Microsoft share the results of their experiments with the earlier version of GPT-4 when it was still in active development by OpenAI. Given GPT-4’s ability to perform multiple tasks on a near-human level of performance, they concluded that “GPT4 is part of a new cohort of LLMs (along with ChatGPT and Google’s PaLM for example) that exhibit more general intelligence than previous AI models”. They do not call GPT-4 an AGI but they see it as “an early (yet still incomplete) version of an artificial general intelligence (AGI) system”.
The Age of AI has begun
”The development of AI is as fundamental as the creation of the microprocessor, the personal computer, the Internet, and the mobile phone. It will change the way people work, learn, travel, get health care, and communicate with each other. Entire industries will reorient around it. Businesses will distinguish themselves by how well they use it”, writes Bill Gates as he declares the beginning of the age of AI. Apart from that, Gates imagines how AI can transform productivity, healthcare, and education while acknowledging the potential risks of powerful AIs.
Pause Giant AI Experiments: An Open Letter
Future of Life Institute published an open letter calling all AI labs to immediately pause for at least 6 months the training of AI systems more powerful than GPT-4. At the time I am writing this, the letter has been signed by over 1000 people, including Elon Musk, Steve Wozniak, Yuval Noah Harari, Yoshua Bengio, Andrew Yang, Max Tegmark and other scientists, business leaders and AI researchers.
AI could replace equivalent of 300 million jobs - report
Goldman Sachs published a report that states that AI could replace the equivalent of 300 million full-time jobs. The report notes AI's impact will vary across different sectors - 46% of tasks in administrative and 44% in legal professions could be automated but only 6% in construction and 4% in maintenance, it says.
The Unpredictable Abilities Emerging From Large AI Models
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit an interesting behaviour - once they reach a certain threshold of complexity, their functionality skyrockets. In other words, bigger models can do more than smaller models. This is an interesting observation that occupies the minds of some AI researchers who study this emergent behaviour and try to predict what new skills LLMs can acquire as they grow in size.
▶️ Nvidia's GTC Event: Every AI Announcement Revealed in 11 Minutes (11:02)
The theme of this year’s Nvidia’s GTC event was generative AI and what Nvidia offers to advance the field, from new servers and supercomputers to Nvidia’s generative AI services to new partnerships integrating this technology into products and services from likes of Shutterstock, Adobe and cloud providers. I’m linking to CNET’s summary of the event. If you have time, here is the full 1 hour and 17 minutes long presentation.
Levi’s will ‘supplement’ human models with AI-generated fakes
Levi announced a partnership with Lalaland.ai - a company that generates digital models. Levi frames the partnership as a step towards diversity and sustainability. “We see fashion and technology as both an art and a science, and we’re thrilled to be partnering with Lalaland.ai, a company with such high-quality technology that can help us continue on our journey for a more diverse and inclusive customer experience”, says Levi in the press release.
🤖 Robotics
Making mind-controlled robots a reality
Researchers from Australia have created a brain-computer interface (BCI) that allows people to control robots using only thoughts. In cooperation with Australian Army, they demonstrated a hands-free control over a quadruped robot with 94% accuracy using their BCI. "The hands-free, voice-free technology works outside laboratory settings, anytime, anywhere. It makes interfaces such as consoles, keyboards, touchscreens and hand-gesture recognition redundant," said Professor Francesca Iacopi, co-creator of this device.
▶️ How agri-robotics will change the food you eat (9:38)
Agricultural robotics and artificial intelligence are changing how we farm, from day-to-day practices to selecting new crop varieties. In this talk, Katherine James gives an overview of how agri-robotics is changing the way we interact with crops, how this will change the crops themselves and, ultimately, how this will allow humans to focus more on things which require the “art-of-being-human”.
▶️ Transmission // Оne-take story shot entirely on a FPV drone (0:52)
This short video has been shot entirely using only a first-person view (FPV) drone. It looks amazing and I hope this short will inspire more creative uses of drones in cinematography.
Metal-Detecting Drone Could Autonomously Find Landmines
Researchers at Autonomous Systems Lab at ETH Zurich have created a metal-detecting drone designed to locate landmines. The drone can fly very close to the ground and detect metal with an attached metal detector. I can imagine a future in which a swarm of such drones fly over a minefield and mark landmines or explosives for humans or other robots to deal with.
🧬 Biotechnology
Forget designer babies. Here’s how CRISPR is really changing lives
It’s been over 10 years since CRISPR entered the genetic engineering toolbox and it is already changing lives. But instead of creating attention-grabbing designer babies, CRISPR is saving the lives of people suffering from genetic disorders, like sickle cell disease, with more therapies becoming available soon.
Meatball from long-extinct mammoth created by food firm
One of the things proponents of lab-grown meat said could be possible with this technology will be an opportunity to taste exotic or even extinct animals’ meat. Well, the latter has become a reality, thanks to a startup that made meatballs made from lab-grown mammoth meat.
New CRISPR tool reversed blindness in mice — permanently
Chinese scientists have created a new gene therapy that cures retinitis pigmentosa - a rare genetic disorder that results in blindness. The treatment has been proven to work in mice and it seems to be a permanent fix - the mice retained vision well into old age.
H+ Weekly is a free, weekly newsletter with the latest news and articles about AI, robotics, biotech and technologies that blur the line between humans and machines, delivered to your inbox every Friday.
Subscribe to H+ Weekly to support the newsletter under a Guardian/Wikipedia-style tipping model (everyone gets the same content but those who can pay for a subscription will support access for all).
You can follow H+ Weekly on Twitter and LinkedIn.
Thank you for reading and see you next Friday!