Six new AI models worth your attention - Sync #550
Plus: Gemini 3 Flash, GPT-5.2-Codex; ChatGPT Images; iRobot files for bankruptcy; how a 27M model beat ARC-AGI; AlphaEvolve on Google Cloud; Waymo in talks to raise $15B
Hello and welcome to Sync #550!
This week, we’re taking a look at some new AI models released recently that may have been overshadowed by bigger launches, but still deserve attention.
Elsewhere in AI, Google released Gemini 3 Flash and brought AlphaEvolve to Google Cloud, while OpenAI launched GPT-5.2-Codex and ChatGPT Images. Additionally, OpenAI is reportedly in talks over new funding rounds and is launching an app store within ChatGPT. We also have a story on how Tilly Norwood, an AI actress, was created, as well as who was Broadcom’s mysterious $10 billion customer.
Over in robotics, Roomba maker iRobot has filed for bankruptcy, Waymo is in talks to raise $15 billion, and Japanese researchers have built a musculoskeletal robot dog.
Beyond that, we explore solar geoengineering start-ups getting serious, what it’s like to be a BCI pioneer, how small AI models conquered ARC-AGI, and more.
Enjoy!
Six new AI models worth your attention
The past few weeks have been packed with major AI model releases. Gemini 3 Pro and Gemini 3 Flash, Claude Opus 4.5, GPT-5.2 and DeepSeek-V3.2 have understandably grabbed most of the attention. But they were not the only launches. Below are six recently released models worth paying attention to, with all but one of them being open.
Nvidia Nemotron 3
Nvidia’s Nemotron 3 is a new family of open models aimed squarely at agentic, multi-agent systems—the kind of setups where multiple specialised agents share context, call tools, and collaborate over long tasks. The family includes three variants designed for different roles in those workflows:
Nemotron 3 Nano (~30B parameters; ~3B active per token): optimised for high-throughput tasks such as code debugging, content summarisation, retrieval-augmented Q&A and lightweight assistant work. Nvidia claims up to 4× higher token throughput than Nemotron 2 Nano while producing up to 60% fewer reasoning tokens, which can meaningfully reduce inference cost.
Nemotron 3 Super (~100B): positioned for multi-agent applications where many agents need to work in parallel on complex problems while keeping latency low.
Nemotron 3 Ultra (~500B): the high-capacity option, intended as a heavyweight reasoning engine for the most demanding workloads.
Under the hood, Nemotron 3 uses a hybrid Mamba–Transformer mixture-of-experts design, combining efficient long-sequence modelling with targeted attention and sparse expert routing. (If you are not familiar with Mamba, there is a good explainer here.) Across the family, Nvidia highlights a 1M-token context window and high throughput—useful when agents share a long-running workspace or operate over large codebases and document collections.
Nemotron 3 Nano is available now via Hugging Face, selected cloud providers and Nvidia’s NIM microservices. Super and Ultra are expected to be released in the first half of 2026. Nvidia is also releasing open datasets, reinforcement-learning environments and training recipes. The point is not just “open weights”, but something closer to an open model stack that teams can inspect, adapt and extend on their own infrastructure.
Kimi K2 Thinking
Kimi K2 Thinking is Moonshot AI’s new flagship “thinking agent”: a trillion-parameter, open-weight mixture-of-experts model built to reason step by step while actively using tools such as search, code interpreters and browsers. Moonshot positions it as a long-horizon system, able to keep a coherent line of reasoning over hundreds of steps and execute roughly 200–300 sequential tool calls without human intervention.
On Moonshot’s own evaluations, K2 Thinking reports strong results on agentic and reasoning benchmarks, including 44.9% on Humanity’s Last Exam (HLE), 60.2% on BrowseComp, and 71.3% on SWE-Bench Verified. Moonshot claims these scores put it at or above leading proprietary models on several long-horizon search and coding tasks.
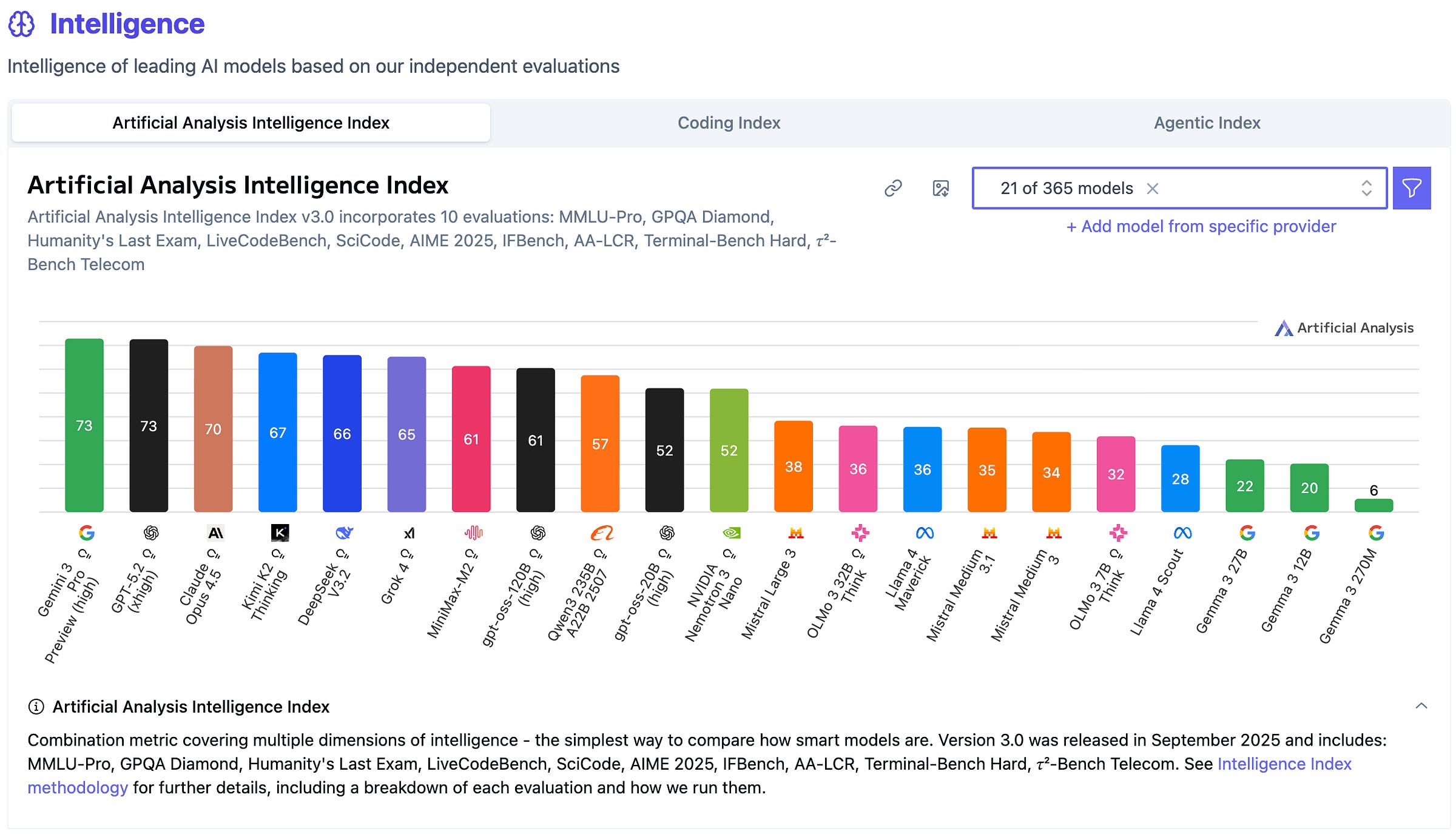
Third-party evaluation points in the same general direction. Artificial Analysis assigned K2 Thinking an Intelligence Index score of 67, the highest for an open-weight model in their rankings at the time and second only to GPT-5.
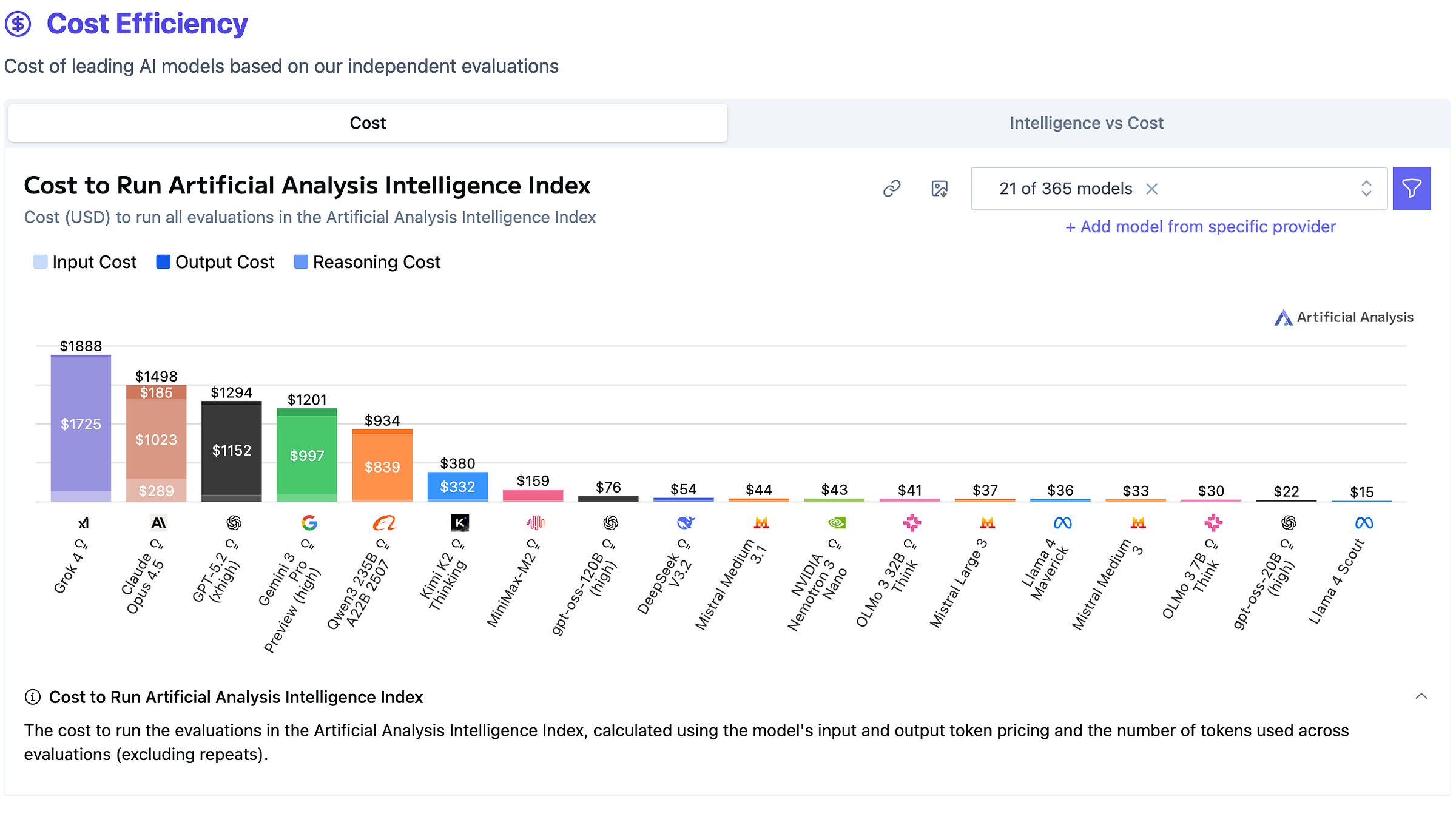
Technically, K2 Thinking supports a 256k-token context window and is released natively in INT4, using quantisation-aware training to keep performance high while making a trillion-parameter model practical to run. Artificial Analysis notes that K2 Thinking generated an unusually large number of tokens to complete their test suite, which can increase latency and cost per run compared with more concise models. Even so, aggressive token pricing can keep total costs competitive in practice.
Kimi K2 Thinking is available on Hugging Face under a modified MIT-style licence: it permits commercial use, with a light attribution requirement that applies only at very large scale. Overall, the release strengthens the case that open-weight models can compete near the frontier on reasoning and tool-using workloads—while remaining easier to inspect, self-host and adapt than API-only systems.
FunctionGemma
FunctionGemma is the latest addition to Gemma—Google’s family of open-weight models. Based on Gemma 3 270M, it is tuned specifically for function calling: converting natural-language requests into structured API calls that software can execute locally on-device. Think of it less as a chatbot and more as a compact “action engine” for agents on phones, browsers and edge hardware.
Function calling is where small on-device models often fall apart: they can be fluent, but unreliable when asked to produce exact structured outputs. Google reports that on its internal Mobile Actions benchmark, a generic small model achieved around 58% accuracy, while FunctionGemma reached roughly 85% after fine-tuning, closing much of the gap to larger cloud models while remaining fast and lightweight.
Google envisions two use cases for FunctionGemma:
Fully offline assistant: translate commands like “Create a calendar event for lunch tomorrow” or “Turn on the torch” into precise OS-level actions without sending data to the cloud.
Local router in a hybrid system: handle routine, high-frequency actions on-device, and only escalate genuinely complex requests to larger models (for example, Gemma 3 27B or other cloud LLMs).
Google has released the model weights alongside a full training recipe, including the Mobile Actions dataset and guidance for fine-tuning and response sequencing. FunctionGemma is available on Hugging Face and Kaggle.
Meta Segment Anything Model Audio (SAM Audio)
SAM Audio is Meta’s attempt to bring the Segment Anything idea—picking out exactly what you want from messy data—into the audio world. In plain terms, it’s a foundation model designed to isolate a chosen sound (a voice, an instrument, a barking dog, traffic noise, etc.) from an audio track or an audio-visual clip using simple prompts.
The most interesting part is how you specify what to extract. Meta describes three prompt types that can be used alone or combined:
Text prompting: type what you want (e.g., “singing voice”, “dog barking”).
Visual prompting: in a video, indicate the person or object producing the sound, and isolate the audio associated with that visual source.
Span prompting: mark a time range where the target sound occurs, helping the model stay locked onto the right source over longer clips.
With SAM Audio, audio editing could become more like pointing and describing than painstaking manual clean-up. If the prompting behaves robustly, SAM Audio could make audio editing feel more like pointing and describing than painstaking manual clean-up. Obvious use cases include podcast editing, quick noise removal from video, and isolating stems in creative workflows
Meta says you can experiment with SAM Audio in the Segment Anything Playground, and the project is also available for developers via an official GitHub repository with inference code and examples.
Mistral OCR 3
After releasing Mistral 3 and Devstral 2, the French AI startup Mistral comes back with Mistral OCR 3, an AI model built to turn messy real-world documents into clean, structured data.
On internal benchmarks, it achieves a 74% overall win rate over Mistral OCR 2 across forms, scanned documents, complex tables and handwriting. According to Mistral, its latest model does not just dump characters, but also extracts text and embedded images and preserves structure, outputting markdown enriched with HTML tables (with proper rowspan/colspan). That makes it well-suited to complex statistical tables, invoices, contracts and technical reports where layout matters. It’s also far more robust to low-quality scans, skew, noise and dense form layouts, and significantly better at cursive and mixed handwriting than OCR 2.
Mistral OCR 3 is available via the Mistral API and through the Document AI Playground in Mistral AI Studio. Typical applications include invoice and form parsing, large-scale archive digitisation, and document-to-knowledge pipelines powering RAG and enterprise search—anywhere that high-fidelity structure and cost per page matter.
Olmo 3.1
Olmo 3.1 is the latest update to the Allen Institute for AI’s (AI2) fully open Olmo family, with an emphasis on transparency and reproducibility. Rather than publishing weights alone, AI2 is pushing what it calls the “model flow”: the full pipeline from training data and code through checkpoints, evaluations and reinforcement-learning recipes.
The release centres on two upgraded 32B models:
Olmo 3.1 Think 32B: a reasoning-oriented model that underwent additional reinforcement-learning training on the Dolci-Think-RL dataset.
Olmo 3.1 Instruct 32B: a stronger chat and tool-use model built using the instruction-tuning recipe that performed well at the 7B scale.
AI2 also refreshes its research-oriented RL Zero 7B line with new Code and Math checkpoints. These runs start directly from the base model without prior instruction tuning, giving RL researchers clean baselines while keeping a clear trace from behaviour back to training signal.
Olmo 3.1 is available on Hugging Face and on GitHub.
To finish off, let’s see how these models compare—both with each other, with the top three frontier models (Gemini 3 Pro, GPT-5.2 and Claude Opus 4.5), and with other open models such as DeepSeek-V3.2, Qwen3 235B and gpt-oss-120B. Below are the results from Artificial Analysis’s Intelligence Index and cost-efficiency metrics. The full comparison can be found here.
If you enjoy this post, please click the ❤️ button and share it.
🦾 More than a human
▶️ Why I volunteered for brain-computer interface research (16:12)
In this video, Scott Imbrie, who became a quadriplegic after a car accident at the age of 22, explains why he volunteers as a participant in brain–computer interface research. Scott takes part in a spinal cord injury research project at the University of Chicago, where he is able to control a robotic arm and hand with sensory feedback. The aim of the study is to restore independence to individuals with spinal cord injuries. His story is one of determination, resilience, and hope that BCI technology will help people like him live a normal life.
Next-Gen Brain-Computer Interface Packs 65,000 Electrodes on One Chip
Researchers have created a new brain–computer interface called BISC, an extremely thin, wireless chip that sits on the surface of the brain and contains over 65,000 electrodes. Unlike current systems that require bulky implants and wires, BISC is minimally invasive while still capturing very detailed brain signals. Early animal studies and initial human trials suggest it could help treat conditions such as epilepsy and, in the future, enable more natural communication between the brain, computers and AI.
🧠 Artificial Intelligence
Broadcom reveals its mystery $10 billion customer is Anthropic
Back in September, Broadcom signed a $10 billion deal for AI chips with a mysterious customer. Now, Broadcom revealed that the mystery customer behind this order was Anthropic, which also placed a further $11 billion order in the same quarter. The chips are Google’s tensor processing units, which Broadcom helps make and which can be more efficient than Nvidia’s for some AI tasks.
Introducing GPT-5.2-Codex
OpenAI has introduced GPT-5.2-Codex, a coding-focused version of its recently released GPT-5.2 model, which the company says is the most advanced agentic coding model to date for complex, real-world software engineering. The model is optimised for long-horizon coding tasks, large-scale refactors and migrations, improved Windows and terminal performance, and stronger vision capabilities.
Gemini 3 Flash: frontier intelligence built for speed
Google has unveiled Gemini 3 Flash, a new addition to its Gemini 3 model family that prioritises speed, efficiency and lower costs while maintaining frontier-level intelligence. According to Google, the new model delivers Pro-grade reasoning with significantly faster performance and reduced token usage, targeting developers, enterprises and everyday users alike. Gemini 3 Flash is rolling out globally across the Gemini app, AI Mode in Search, and Google’s developer and enterprise platforms, where it will become the default model for many users.
OpenAI’s New Fundraising Round Could Value Startup at as Much as $830 Billion
The Wall Street Journal reports that OpenAI is seeking to raise up to $100 billion in a new funding round that could value the company at as much as $830 billion. The fundraising is still in its early stages and is meant to support OpenAI’s rapid expansion and the high costs of developing advanced AI models.
The new ChatGPT Images is here
OpenAI has launched an improved version of ChatGPT Images that, according to this press release, generates images up to 4× faster, follows instructions more accurately, and makes precise edits while keeping key details such as lighting and facial appearance consistent. It also offers improved creative styles, clearer text rendering, and more realistic results, although some limitations remain. The new ChatGPT Images model is now available to all ChatGPT users worldwide and is accessible via the API as GPT-Image-1.5, with Business and Enterprise access coming later.
OpenAI in talks with Amazon about investment that could exceed $10 billion
According to CNBC, OpenAI is in talks with Amazon about a possible investment of more than $10 billion, alongside a deal to use Amazon’s AI chips. The discussions follow OpenAI’s recent restructuring, which gives it more freedom to raise funding and work with partners beyond Microsoft.
ChatGPT launches an app store, lets developers know it’s open for business
OpenAI has introduced an app store inside ChatGPT, letting developers submit apps for approval and use within chat conversations. Following earlier partnerships with major platforms, this move opens ChatGPT to more developers and gives users new ways to complete tasks directly in the app, helping expand its features and keep users engaged.
AlphaEvolve on Google Cloud: AI for agentic discovery and optimization
AlphaEvolve, a Gemini-powered tool from Google Cloud that helps improve algorithms for complex optimisation problems, is now available on Google Cloud. AlphaEvolve works by repeatedly generating, testing and refining code to find more efficient solutions over time. Google has already used AlphaEvolve to improve data centre efficiency, speed up AI training and enhance hardware design, and the tool is now available in early access for businesses across industries such as biotech, logistics, finance and energy.
Why Cursor’s CEO believes OpenAI, Anthropic competition won’t crush his startup
Anysphere, the company behind the AI coding tool Cursor, is not planning an IPO for now, despite reaching $1 billion in annualised revenue and a high valuation, as it focuses on improving its product. CEO Michael Truell said the company is developing its own specialised AI models, adjusting pricing to reflect usage costs, and building tools to help businesses manage spending.
Inside the Creation of Tilly Norwood, the AI Actress Freaking Out Hollywood
This article explores the creation of Tilly Norwood, a highly realistic AI-generated actress, and the fierce debate she has sparked in Hollywood. It examines how Tilly was painstakingly designed using generative AI, the creative and economic ambitions behind her, and the intense backlash from actors and filmmakers who fear AI will undermine artistic integrity and jobs.
Google DeepMind Will Open a Robotic AI Lab in the UK to Discover New Materials
Google DeepMind will open its first UK research lab next year, focused on discovering new materials using AI and robotics. The lab will support research into materials for medical imaging, solar panels and computer chips, and is part of a wider partnership with the UK government.
▶️ How did a 27M Model even beat ChatGPT? (13:15)
This video explores new reasoning-focused architectures such as the Hierarchical Reasoning Model (HRM) and its successor, Tiny Recursive Model (TRM). Both achieve strong performance on difficult reasoning benchmarks such as ARC-AGI despite having only millions of parameters. These models suggest that architectural innovation and recursive reasoning may be more important than sheer model size, potentially signalling a shift in the future direction of AI research.
🤖 Robotics
Roomba maker iRobot files for bankruptcy, pursues manufacturer buyout
iRobot, the company behind Roomba vacuum cleaners, has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in the United States and will be taken private by its main manufacturer, Picea Robotics. Despite generating $682 million in revenue in 2024 and retaining strong market positions in the US and Japan, the company has struggled with falling profits, higher costs from new US tariffs, a heavy debt burden and competition from cheaper rivals.
Alphabet-owned Waymo in talks to raise $15 billion in funding
Waymo is discussing a new funding round that could raise more than $15 billion and value the company at up to $110 billion, more than twice its valuation in late 2024, according to a report by The Information. The Alphabet-owned company plans to use the funding to expand its self-driving taxi service to many more cities in 2026, including its first launch outside the US in London.
MIT researchers “speak objects into existence” using AI and robotics
Researchers from MIT present “speech-to-reality”, a system that lets people create physical objects simply by speaking. Using AI and a robotic arm, the system turns spoken requests like “I want a stool” into real items within minutes, without requiring design or technical skills. The goal is to make making things faster, easier, and more sustainable, bringing the idea of on-demand object creation closer to reality.
1X partners with EQT to roll out humanoids across its portfolio companies
1X Technologies has partnered with investment firm EQT to roll out up to 10,000 of its NEO humanoid robots across EQT’s portfolio companies between 2026 and 2030. The deal marks a shift for 1X from focusing on home use to targeting workplaces such as warehouses, factories and healthcare facilities. EQT says the robots will help companies tackle labour shortages, improve safety and increase productivity, while giving its portfolio early access to emerging humanoid technology.
Ghost Robotics Unveils New Manipulator Arm for the Vision 60 Q-UGV
Ghost Robotics has introduced a new manipulator arm for its Vision 60 robot, allowing it to perform tasks such as opening doors, picking up objects and handling equipment. The lightweight, modular arm gives the robot greater ability to work in both indoor and outdoor environments without losing mobility. Functionally, the arm appears similar to the manipulator offered by Boston Dynamics for its four-legged robot, Spot (the two companies were previously involved in a patent infringement dispute that was settled earlier this year).
Humanoid robots take center stage at Silicon Valley summit, but skepticism remains
This article takes us to the recent Humanoids Summit in Silicon Valley, where experts, engineers and investors came together to discuss the growing interest in humanoid robots powered by advances in artificial intelligence. It explains that while some robots are already being used for entertainment and limited workplace tasks, truly human-like, general-purpose robots are still far from reality due to major technical challenges. The article also highlights differing opinions about the future of humanoid robots and notes that China is currently moving faster than the United States in developing this technology.
▶️ Dog Musculoskeletal Robot (1:05)
Researchers from Japan have developed a dog musculoskeletal robot. Unlike other robot dogs, such as Boston Dynamics’ Spot, this robot mimics a dog’s biomechanics using artificial muscles. So far, the robot appears to be in the early stages of development and cannot move on its own or even maintain an upright posture without support. But perhaps in the future, its descendants will be running like real dogs.
🧬 Biotechnology
Chai Discovery Announces $130 Million Series B To Transform Molecular Discovery
Chai Discovery has raised $130 million in a Series B funding round, which brings its to $1.3 billion. The company uses AI to design drug-like molecules, including for targets that are difficult to treat with traditional methods, helping to speed up drug development. The new funding will be used to expand research, improve its technology and grow commercial partnerships.
💡Tangents
Solar geoengineering startups are getting serious
Solar geoengineering is the idea of deliberately cooling the Earth by reflecting a small portion of sunlight back into space, for example, by releasing particles into the atmosphere. This might sound like a concept straight from science fiction, but there are already companies doing that. This article explores these controversial companies and highlights concerns raised by researchers after Stardust Solutions raised major funding, sparking fears about profit motives, lack of transparency, and the possibility that a single company could affect the entire planet.
Thanks for reading. If you enjoyed this post, please click the ❤️ button and share it!
Humanity Redefined sheds light on the bleeding edge of technology and how advancements in AI, robotics, and biotech can usher in abundance, expand humanity's horizons, and redefine what it means to be human.
A big thank you to my paid subscribers, to my Patrons: whmr, Florian, dux, Eric, Preppikoma and Andrew, and to everyone who supports my work on Ko-Fi. Thank you for the support!
My DMs are open to all subscribers. Feel free to drop me a message, share feedback, or just say "hi!"